Mainframe systems have countless applications running for decades. Most businesses have almost lost knowledge of processes, implementation technology, and business rules. Many migration projects face several mainframe to cloud migration challenges and when some of the risks are not properly mitigated, they do tend to disastrous results.
However, standing still is no option for businesses that aim for constant growth and expansion. The benefits a company gains from cloud capabilities easily override the challenges of the transition.
An effective way to mitigate Mainframe Migration Risks is to understand the risks and ways to reduce them before commencing the process.

Table of Contents
Planning and Estimation Risks
Inaccuracy in planning opens the door for multiple challenges, including delays, incorrect choice of tools, increased cost, and even business disruption.
The answer is to analyze the current and desired states. It helps fine-tune the scope, control costs, and prioritize efforts. The following pointers highlight the essential considerations that help mitigate mainframe to cloud migration challenge during the planning and estimation stage.
- Accurate application profiling, filtering dead code and data, identifying functional relationships, and establishing delivery ownership and scheduling.
- Defining the foundation architecture of the target cloud platform
- Selecting the right tools for source code translation
- Evaluating licensing options and choosing a trusted vendor
- Defining benchmarks for performance, reliability, scalability, security, backup, recovery, and other aspects
Technical Risks
Choosing the right technology stack and tools is the basis of a successful migration project. A mainframe workload has complexity in the unfathomable quantity of code and data, dependencies, batch durations, legacy technology, versions, complicated logic, incomplete or absent documentation, and more.
Mitigating a technical risk is an important cloud migration challenge and the only way to mitigate it, is through rigorous testing to gain POCs. Business analysts must test the tech stack’s capabilities for their enterprise-specific scenarios. The test cases should be of the highest complexity that uncovers the ability of the tools, quality of the outcome, and assists in selecting the right stack.
Infrastructural Risks
The appropriate architecture selection is the backbone of the target system and its function. The choice impacts the computing space and capabilities, integration, visualization, ease of access, network within and outside the enterprise, scalability, backups, operational cost, and more. Consequently, poor architecture selection augments mainframe to cloud migration challenges and risks.
Business analysts and vendors should come together to develop suitable architecture considering enterprise-specific needs. It involves assessing cloud structures (public, private, and hybrid) and their pros and cons. Companies can choose between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS: based on whether they need physical infrastructure, additional services (operating system, runtime environment, middleware software for communication), or all hardware and software for cloud interaction from the vendors.
People’s Risks
Migration projects are also change projects that bring massive cultural changes, opening substantial mainframe to cloud migration challenges. Moving to new system architecture is often met with significant resistance from the workforce and a need for support from senior management and stakeholders.
The following steps can help mitigate people’s risks and assist the migration change.
- The CIOs should make a solid case for bottom-line growth through migration. They can highlight the benefits of migration in terms of bottom-line enhancement and OPEX and CAPEX reduction.
- Include the mainframe team in defining migration criteria and organizing dedicated training.
- Include the IT team with open-source and cloud skills to guide the transition.
- Create change champions who will be the torch bearers and spokespeople for the change initiative.
- Include the user group as part of the decision-making and design process from the planning stage.
- Creating cross functional teams with clear deliverables can be a great motivator.
- Roping in experts both and cross training them in the source and target technologies can be a force multiplier in initiating the change at a rapid pace.
Maintenance Risk and Complexity
Upgrades, updates, and patches in the tools and software resources released during migration can impact their compatibility, integration, and interaction.
Augmentation of new capabilities or change requests often requires reallocating resources and changes in priorities and timelines. The requirement of code-level changes further complicates the process and adds immensely to the Mainframe Migration Risks, especially in private clouds.
The solution is to install the upgrades and patches to maintain overall performance and regular asset consumption. Business analysts need to jot down a detailed change management strategy during the planning phase to handle every change request with the most negligible impact on the migration process.
Stability and reliability risks of the target platform
One of cloud architecture’s fundamental attributes is its elasticity, allowing it to perform with varying loads. It handles the extreme load in terms of storage, bandwidth, or the number of users by adding more resources and consolidating fewer resources as the load decreases.
The CaaS (Container As A Service) model further makes load handling cost-effective. However, misjudgment in the capabilities of the target platform results in frequent failures and slower recovery and is among the most often overlooked mainframe to cloud migration challenges.
Stress testing the cloud architecture ensures its stability and reliability by:
- Validating the responsiveness of the new platform under extreme load
- Analyzing its performance with multiple users simultaneously
- Benchmarking the cloud’s maximum traffic handling capacity
Availability Risks
Lost, corrupted, or destroyed components during migration can make data or functionalities unavailable. The availability risks spawns additional mainframe to cloud migration challenges, such as losing business operations, revenue generation, and reputation.
The answer to mitigating this risk is backup and fault tolerant processes. Backup replicates vulnerable business-critical components that the enterprises can recover in case of unavailability. Business analysts should design a detailed blueprint as a robust fault-tolerant strategy that guides work continuity whenever some parts are unavailable.
It encourages reevaluating the infrastructural requirements and rectifying and optimizing the processes. This alternate arrangement provides sufficient cushion to locate and debug the issue while keeping the system usable.
Scalability Risks
Scalability helps businesses stay competitive and agile with increasing users and requests. However, it is also among the crucial but often overlooked mainframe to cloud migration challenges, as most companies misunderstand the cloud as infinitely scalable.
To ensure scalability, do answer the question about what you need to scale,
- memory,
- storage,
- or processing power
and to what extent. IT administrators must conduct ongoing APM and NPM to measure the number of users, memory storage, CPU load, and response time. Such testing allows for assessing and maintaining the application’s performance when it scales up or down.
Risks Related to The Project’s Pace
Mainframe migration can typically take several months to complete. A slower project can further increase the complexity and cost and add vulnerabilities to areas, including planning, maintenance, people, and others.
The team must accelerate the project to reduce mainframe to cloud migration challenges associated with slower shifts. Such rapid migration calls for de-risking with greater emphasis on testing to ensure accuracy.
It requires rigorously testing the mainframe and migrated components and iteratively migrating the tested components. It facilitates the rapid and reliable move to the clouds while mitigating the risk of collapse in later stages.
Security Risks
Data is the lifeblood of enterprises, especially when moving to the digital realm. Moving the tremendous amount of mainframe data welcomes several security threats, particularly during transit. Most companies (57%) consider security complexities the biggest challenge in cloud adoption.
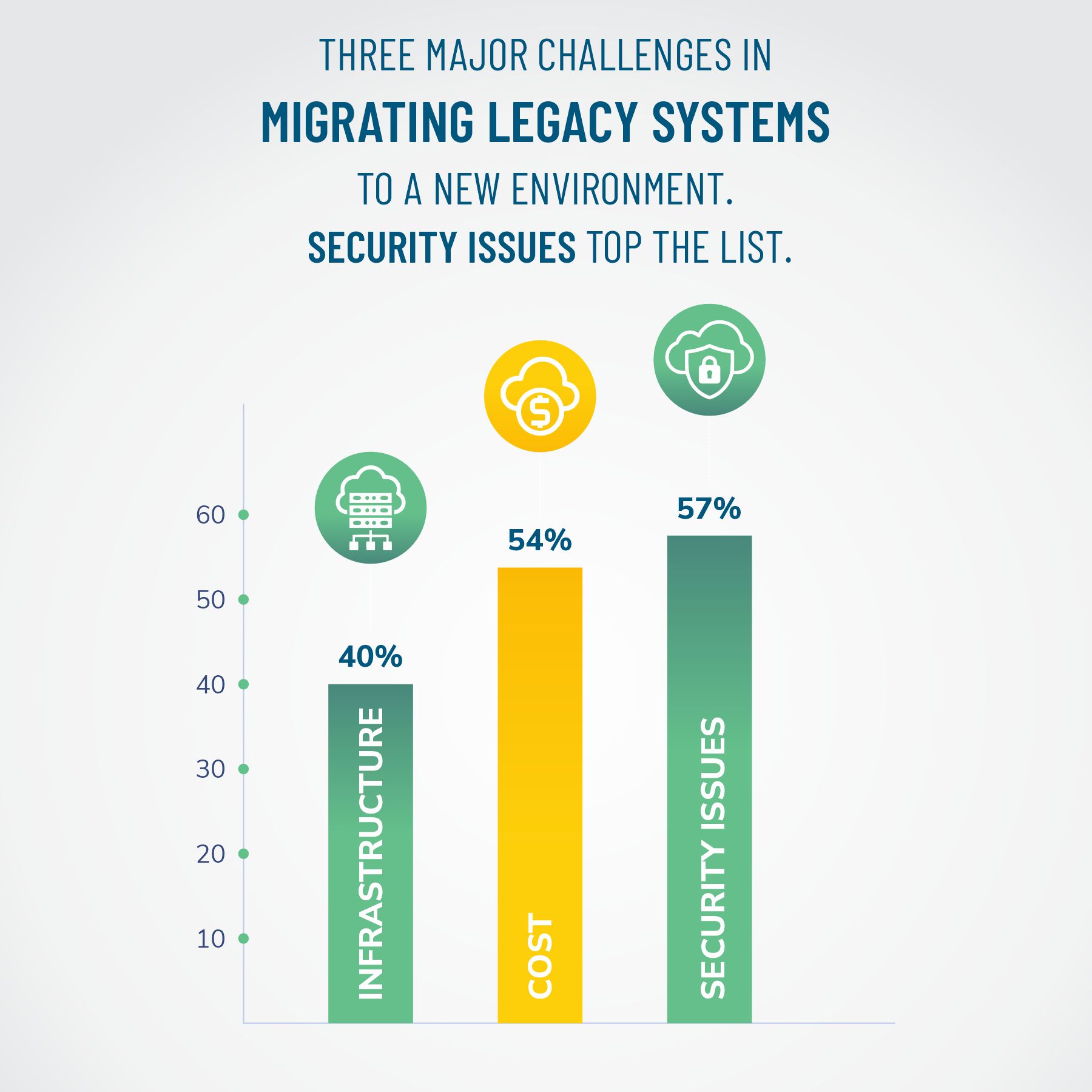 Ensuring Data security demands exceptional expertise from industry whizzes like Kumaran Systems to evaluate existing data for profiling, compliance, and safe transfer. The team at Kumaran Takes the following steps to mitigate Mainframe Migration Risks related to security while ensuring accessibility and availability.
Ensuring Data security demands exceptional expertise from industry whizzes like Kumaran Systems to evaluate existing data for profiling, compliance, and safe transfer. The team at Kumaran Takes the following steps to mitigate Mainframe Migration Risks related to security while ensuring accessibility and availability.
- Assessment and profiling data for migration and identifying safely disposable data.
- Understanding data safeguard compliance requirements concerning finance, government, and other regulatory bodies.
- Controlling data access and duplication
- Encrypting transiting data and wiping the retiring storage
- Evaluating the impact of transferred or deleted data on the remaining data center.
Inadequate Application Performance
While transferring applications to the cloud architecture poses several Mainframe Migration Risks. It can cause IT discontinuity, disruption, and deviation from the established SLAs. Applications delivering less than desired outcomes can be seriously taxing for enterprises.
The following steps help maintain applications’ performance over cloud infrastructure and mitigate this risk.
- Reckon customer usage patterns, bandwidth consumption, complexity level, and distribution to establish the current application’s baseline.
- Comprehend the cloud application’s performance related to established baseline and proactive issue redressal.
- Constant performance monitoring to address application, network, and infrastructural issues
- Monitor application SLAs to assess the impact of changing infrastructure and technology
Data Accuracy Risks
Legacy systems have numerous interdependent applications and datasets. Migration processes often keep some applications on-premise and directly shift or re-engineer other applications as required. It also uses several COTS from various vendors for testing, data transfer, and more. A ballpark integration, interaction, and compatibility assessment can induce additional mainframe to cloud migration challenges.
Thinking through all these issues before commencing is the solution. A phased shift also excellently mitigates integration risks.
- First, shift the applications compatible with cloud and align their interaction with the legacy applications.
- Next, decommission obsolete applications and re-engineer others as required.
Migrating massive datasets attributed to mainframe systems can lead to non-factual and non-compliant data post-migration. Enormous volume, tedious classification and testing, and application stability issues further complicate validating the quality and correctness of the migrated data.
The migration team must establish the validation criteria and assess the impact on ETL processes and analytics. Bulk migration testing, incremental ETL testing, and analytics testing can help reduce other mainframe to cloud migration challenges.
Data Loss While Transitioning
Data loss is a typical migration risk and the biggest nightmare for companies. The primary factors contributing to data loss are missing or corrupt files, accidental deletion due to human error, insider threats, power outages, and security breaches at the data center.
A way to combat these risks is to create backups and deploy stringent access control and multi-factor authentication. Enterprises can also utilize multiple cloud providers and distribute independent replicas on each as a backup. It helps recover quickly if a specific provider’s cloud fails suddenly.
Missing Functionality or Application
Most legacy applications are strongly coupled with each other or with the system and any disruption can lead to additional mainframe to cloud migration challenges. Inadequate application migration can cause functionality loss, security threats, and scalability and compatibility issues.
Kumaran Systems offers pre-migration, migration, and post-migration testing strategized according to the scope and dependencies of the application. Some of the best practices include:
- Code analysis and dependencies mapping
- Programs and subprograms identification
- Impact analysis and decoupling
- Grouping code-sharing applications for the same migration wave and limiting calls between the cloud and on-premise ecosystems
- Incremental migration, wherever possible
Operational Risks
Mainframe systems host petabytes of data and millions of lines of code, a perfect recipe for errors. The increased human intervention significantly increases the project’s complexity and room for glitches. Such mainframe to cloud migration challenges are mostly underrated but can cause high costs and delays.
Automation is the best solution to deal with operational errors. Different vendors (AWS, Azure, Oracle, and Google) offer multiple automation tools to simplify migration processes. Some commonly supported automations are testing (CI/CD pipeline), data transfer, backups, data validation, code refactoring, defining business rules, and applying migration rules.
Risks to User Experience
Navigating to clouds is a mammoth change that creates anxiety and uncertainty among the workforces. If the user interface is not seamless, logical, and intuitive, it further escalates the resistance and deters productivity.
Following best practices in UX design can soothe the transition process and mitigate this risk.
- Design clean and straightforward UX with a focus on essential elements.
- Make it consistent, transparent, intuitive, and efficient.
- Use icons, breadcrumb links, and graphical cues to add navigation-supporting context.
- Create logical progression for seamless flow.
- Assist users with documentation, pop-ups, and video tutorials.
- Deliver reports and other outputs with intuitive visualization.
- Optimize for a larger and faster workload.
Scope Creep
Scope creep is an alarming but underrated issue that can give rise to several mainframe to cloud migration challenges. It often begins with a minor adjustment but blurs the definition of needs, goals, vision, and responsibilities. The result can be significant delays or incomplete projects.
Meticulous planning is the best way to mitigate scope creep. Business analysts should envision the desired state and weigh all possibilities with the cloud infrastructure before planning. They should jot down requirements, goals, milestones, deliverables, reports, success criteria, and every possible variable in executable and referenceable documents.
Take the next step: Migrate with confidence
Kumaran Systems has been a trusted partner in legacy applications migration over decades.
Businesses can save millions of dollars and benefit from exceptional cloud capabilities to gain an unprecedented competitive edge by migrating their mainframe system with our help.
The mainframe to cloud migration challenges can be mitigated with a trusted partner like Kumaran Systems.
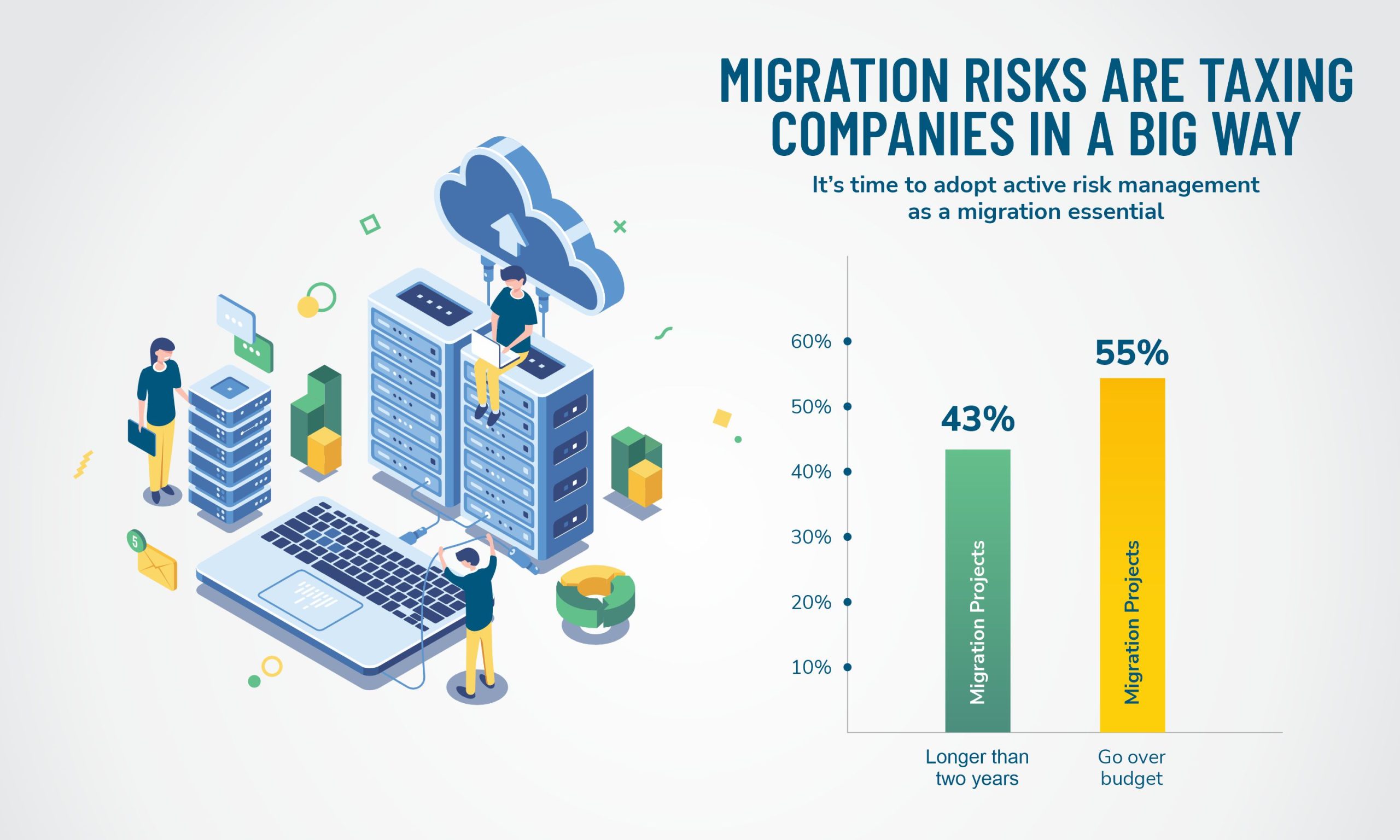 Understanding possible risks and their mitigation solutions are imperative in such scenarios. Additionally, partnering with industry leaders like Kumaran Systems proves a boon for businesses. Our expertise at every phase, from planning to execution and monitoring ensures a successful migration journey.
Understanding possible risks and their mitigation solutions are imperative in such scenarios. Additionally, partnering with industry leaders like Kumaran Systems proves a boon for businesses. Our expertise at every phase, from planning to execution and monitoring ensures a successful migration journey.



