Legacy systems’ compatibility with modern systems diminishes with ever-expanding digital changes. As a result, businesses are rapidly migrating away from them to get greater flexibility, scalability, and agility while saving money. By migrating to a proven strong cloud platform, it enables the deployment of innovative apps and the delivery of superior user/customer experiences and far more reliant performance.
The concern now is what is the best mainframe migration project plan for a successful migration.
The answer indwells two factors: teaming up with experts who have trail-blazed several such projects and picking the right tools to automate key migration steps. Here is a comprehensive guide from the experts at Kumaran Systems, who have spearheaded many migration endeavors to ensure migration readiness and achieve prodigious outcomes.
Table of Contents
Mainframe Migration Project Plan
Today, migration projects are at the core of the enterprise’s business strategies, drastically affecting critical business applications. Thorough planning is crucial for understanding the current standing and envisioning the future state.
Checklist For Mainframe Migration Project Planning:
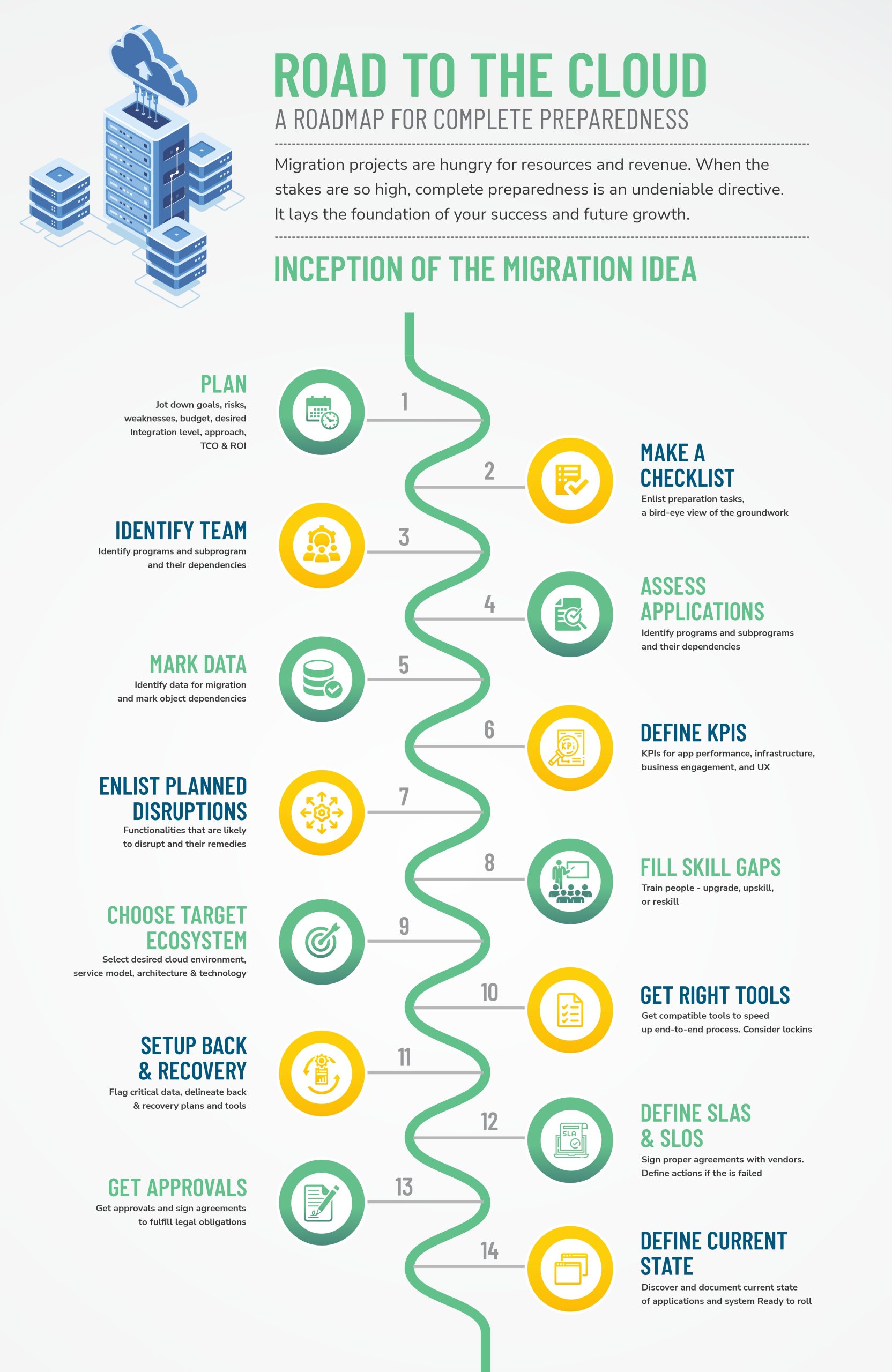
Define objective
A pivotal catalyst for any mainframe migration project plan is the alignment with overarching business goals. Legacy systems lack vertical scalability and agility and can stifle innovation. These factors can quickly push businesses out of competition. Attaining these abilities to meet today’s dynamic customer needs and fluctuating market trends are common goals business leaders aim for in their migration projects.
There can also be other reasons for enterprises to gravitate towards modernization. Businesses choose to shift due to insufficient knowledge/talent of mainframe systems, high operational and maintenance costs, and other reasons.
It is crucial to define the migration goals precisely. It helps identify the KPIs and validate them to keep the project aligned with the overall business objectives.
Pick suitable architecture
Compare platforms for performance, security, tools, industry fitment and platform roadmap. It is imperative to define the foundational target cloud architecture during mainframe migration project planning. It requires matching platform features and tools such as user management, performance, security, compliance, process automation, and more to the enterprise’s needs. Architecture also helps in designating operational security, logging, and network specifications.
Adopt a suitable approach
Weigh need, complexity, capability to follow selected approach.
Defining the migration approach is critical as it determines application downtimes. This strategic mainframe migration project planning helps in anticipating the disruption and consequent preparations to mitigate its impact. Businesses often adopt one or a combination of the following approaches to keep essential applications operational.
- The Big Bang migrates the entire system at one time. The older one goes offline once the new system is up.
- The Parallel involves maintaining both systems until the migration is complete and validated.
- The Phased migrates legacy systems in increments, often on a per-volume, per-module, or per-subsystem basis.
Ascertain integration level
Integration level (shallow/deep) drives your strategy selection (From 6R).
Enterprises often choose one of the 6R migration strategies: Rehost, Refactor, Replatform, Repurchase, Retire or Retain. It ascertains how much work goes into modifying the applications or redoing the applications to perform adequately in the new climate.
- Shallow integration involves moving applications with minimal adaptation to get them run on the cloud. It is faster but often fails to draw full cloud potential.
- Deep integration involves major application modifications such as dynamic load-balancing or auto-scaling to utilize full cloud capabilities.
Identify risks and weak spots
Identify risks, make mitigation plans, & define quick action for resolution.
Identifying risks and having plans to resolve them is quintessential in preparing for the project’s success. It helps to initiate timely action and mitigate their impact. Some of the common migration risks are:
- Application and workload complexity
- Application and data dependencies
- Compatibility of tools and applications during and post-migration
- Hitches in comprehending server modification history
- Difficulty in meeting the mobile users’ needs
- Team resistance
- Support from stakeholders
Define expected ROIs
Migration is expensive. Assess TCO & ROI to ensure profitability.
Assurance of profitability is crucial to begin an investment-intensive migration project. In the discovery phase, enterprises must evaluate detailed app specifications, optimum tech stack, architecture overview, resource allocation, and project timelines among others. They must estimate TCO and ROI in the short and long term.
Mainframe migration preparation checklist
A quick mainframe migration project plan checklist after the initial groundwork provides a birds-eye view of the project. It helps evaluate the project’s readiness and the preparations that still require supervision. The following questions help in providing some degree of foresight on the same.
How big is the migration project?
– How many lines of code?
– How many applications?
– What type of documentation exists?
– When is the lease of the mainframe expiring?
How long will the migration take?
– This is a function of the complexity of the project, technical know-how, and resources availability for such projects.
What is the estimated ROI?
How much data is required to move?
Will the system integration and interfacing be the same as before migration?
How many resources and tools are available?
– Proven automated tools
How to maintain the process flow and minimize downtime?
What will be the security parameter and processes to achieve them during and post-transition?
Identify the team
In a successful mainframe migration project plan, having the right experts on board is pivotal. Having the right people on board means the battle is half-won. Getting the experts early in migration helps define roles and responsibilities. While the specific expertise required depends on the cloud platform and applications involved, the project is led mainly by migration architects. Other required professionals are:
- Business analysts
- Functional Experts
- App developers / Coders / Programmers
- If the tech team has exposure to both the technologies, it would be ideal.
- PMO (Project management team)
- Infrastructure specialists for network, server, and app.
- Security/compliance officer
Assess application dependencies
In any mainframe migration project plan, it’s vital to assess and identify the legacy applications for shifting. Apps can be mission-critical, business-critical, customer-facing, and others. Categorization helps in prioritizing apps and determining the flow of migration.
Legacy applications are strongly coupled and have intricate interfacing. Any lacuna in maintaining or resolving these dependencies in the new environment can lead to security threats, compatibility issues, and functionality loss. The following steps help dodge such pitfalls.
- Identify programs and subprograms.
- Decouple, map, and create a dependency tree.
- Group code-sharing applications
- Limit cross-platform calls
- Incremental migration and impact analysis
Factors to demonstrate application readiness
As part of the mainframe migration project plan, it’s important to recognize several legacy applications are not optimized for the cloud. As cloud often calls for higher functional capacity, these apps can become inefficient in the new environment. In addition to assessing application inventories and dependencies, the following factors also help verify application readiness.
- Business factors: application criticality, content impact, and regulatory exposure
- Software factors: versioning and update requirements (for OS / Server), monitoring needs, level of virtualization.
- Application factors: app integration (custom/packaged), networking needs, storage needs.
Mark data dependencies
Complex legacy codes have several root or parent objects referring to individually derived objects, including taking care of interdependencies while migrating a parent object to the new ecosystem.
These mutually shared responsibilities are also subject to change over time during import and export. Business analysts must cognize such possibility of variation due to daily activities to ensure data integrity during migration. Enterprises can use tools that automatically detect and export object dependencies while moving to cloud.
Define KPIs in Mainframe Migration Project Plan
Key Performance Indicators or KPIs are parameters to assess the outcomes against the specified requirements. These parameters ensure that the migration project meets all the required performance criteria and delivers as anticipated. Some of the commonly referred migration categories and their related KPIs are:
- User experience: Page load delays, response time, session duration
- Application performance: Availability, throughput, error rates, application performance index
- Infrastructure: Memory usage, CPU usage, disk performance, network throughput
- Business engagement: Engagement rate, cart additions, conversions, NPS scores.
Elucidate planned disruptions
Although enterprise leaders ensure the availability of business-critical applications during migration, avoiding disruption altogether is often tricky.
Analysts must identify functionalities likely to disrupt while migrating and mitigate the cutover time for the end user. Companies must adopt multiple strategies to seamlessly shift critical applications, such as POS and credit card authentication.
Fill the skill gap
Migration projects involve two extremely contrasting IT environments: legacy mainframe systems and the cloud. Collaborating with experts from both worlds is crucial for the project’s success. Enterprise leaders must have the right expertise on board and map them precisely to different project phases of the mainframe migration project plan.
The cloud environment is a complex ecosystem constantly evolving and requires perpetual skill upgrades. It often calls for hiring a cloud migration consultant, a specific cloud expert, and other professionals to educate the in-house team. Proactive measures like setting-up cloud institutes and rewarding certifications can help significantly.
Choose the target ecosystem
Designing the target cloud-based ecosystem is a challenging endeavor that involves critical decisions on the following.
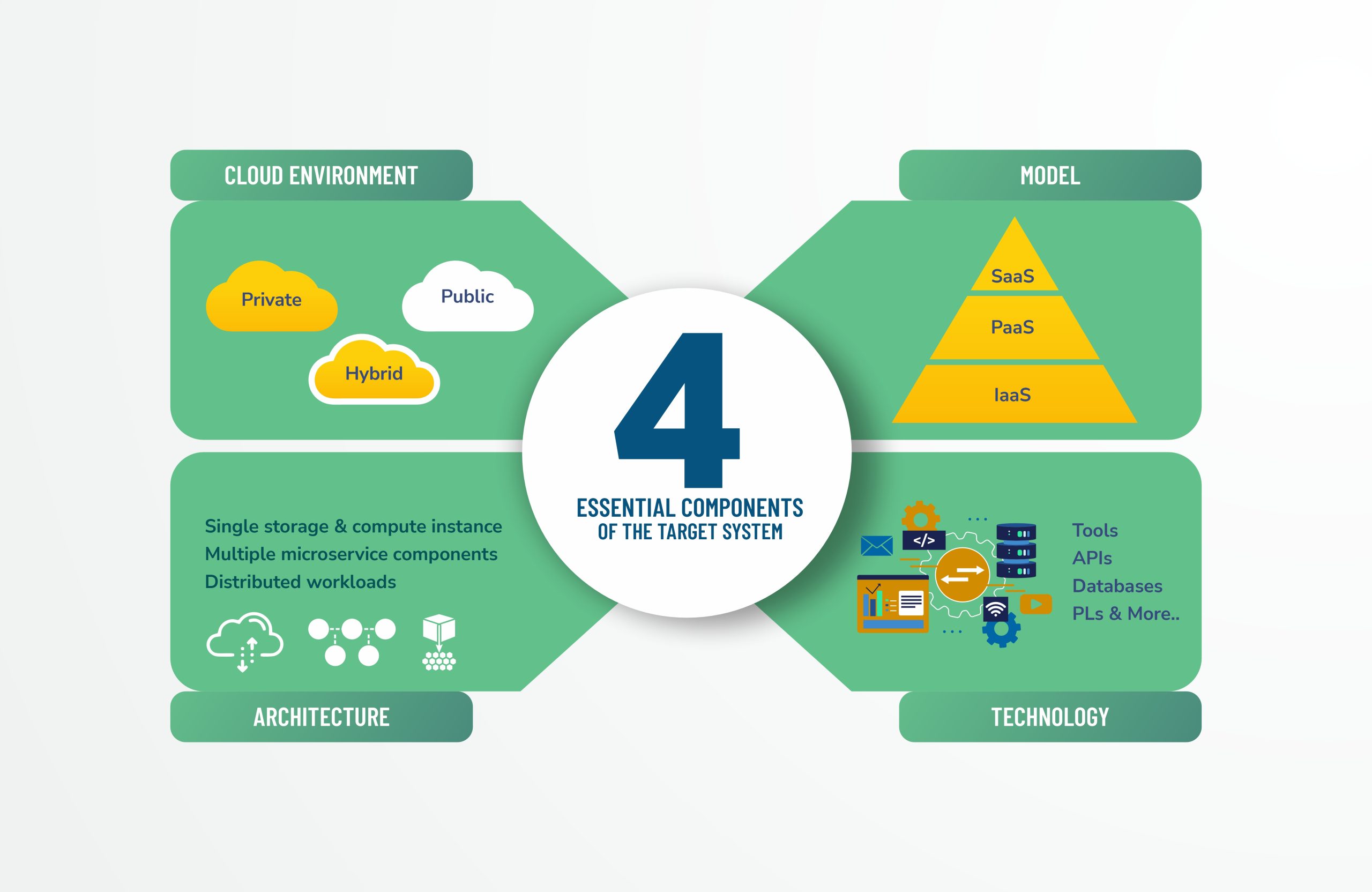
Environment
An ideal environment must reflect and harmonize with long-term business goals, keeping in mind the investments. Major cloud environment options are:
- Private clouds are small-scale clouds that operate with their existing data center infrastructure. They require significant technical and budgetary commitments.
- Public clouds are extensively scalable from third-party providers with a global reach. They offer a wealth of services available on a pay-per-use model.
- Hybrid clouds combine the capabilities of private and public environments providing greater control with incredible scalability and flexibility. Many businesses also consider maintaining hybrid infrastructure on-premises and over the cloud.
Model
Models define the approach of accessing services classified based on user control and convenience.
- The IaaS model assembles traditional infrastructural elements such as servers, storage, and more to host the organization’s workload.
- The PaaS also includes software components along with hardware. These components include development tools, databases, runtimes, and other tools that replace the existing ones.
- The SaaS providers offer ready-made applications and handle complete workload development and maintenance.
Architecture
Businesses can choose straightforward architecture hosting single storage and compute instances. Or a complex one, supporting multiple microservice components or mission-critical distributed workloads. An intelligent architecture design requires rigorous testing to validate its functionality after deployment.
Technology
Business analysts and the IT team collaborate to finalize the tech stack for the project. It includes decisions about OS, programming language, framework, front-and-back-end tools, APIs, and databases. The chosen cloud environment and cloud service provider often guide this decision.
Get the correct migration tools
Automation tools are a boon for migration, which takes much heavy lifting and simplifies the mainframe migration project plan. Tools can automate planning, tracking, testing, quality control, error handling, backups, analytics, reporting, license validation, and more.
Tools are available as open source, come with the cloud environment, and are also proprietary, provided by the service providers. Kumaran Systems offers several tools, such as a business rule extraction tool, to enhance workload efficiency and productivity.
The following pointers help select the right tools.
- Level of support it lends during the end-to-end migration journey
- Compatibility with the chosen cloud designation
- Possibility of a pre-migration assessment
- Role in migrating application, data, content, or workload
- Features to unearth insights to enhance performance on the cloud
Set up backup and recovery plans
While shifting tons of applications with even more test executions, backup is inevitable. Businesses can consider the following steps to set up a robust backup plan.
- Adopt the tools and best practices of the chosen cloud environment.
- Delineate backup methodology and frequency.
- Flag critical data and instructions for the protection plan.
- Assess recovery plans and expected latency.
- Establish disaster management plans to deal with service disruption, cyber-attacks, and more.
- Automate backups with flexible and reliable tools.
- Test the waters with repeated assessments of the backup strategy.
Define SLAs and SLOs
The enterprises must have a technical service performance contract with the providers and vendors. They provide required KPIs and negotiate related SLOs. Automated services enforce these SLOs and generate alerts when the agreed actions fail.
Most cloud providers have standard SLAs defining the way they provide services. Enterprise leaders must review these agreements with their legal counsels to establish a good-faith contract between the parties.
Signing these documents before accepting the services helps set the benchmark for what enterprises need and how the providers will deliver.
Get state approvals and agreements
For regulated industries complying with state, federal, and industry regulations is imperative. Having the required approvals and legal signoffs saves heavy penalties and disciplinary actions. These regulations are also a protective shield for the enterprise and its customers.
However, compliance is often challenging due to the ever-changing landscape. Anything from a shift in political power to an economic downswing triggers regulatory responses. Enterprise leaders and legal counsels must stay abreast of regulations and guarantee compliance.
Jot down the current application state
A thorough assessment of the migration viability of each application is paramount. It helps in prioritizing the candidate applications and ascertaining a smooth transition. Consider the following factors while scrutinizing applications’ current state.
- Inventory, including data, library, test case results, attributes, and dependencies.
- Features and functionality the app must continue delivering in the new climate.
- Frequency of changes for innovation and adjustments and their impact
- Complexity in terms of availability of documentation and developer, duration of use, and number of updates
- Criticality related to the dependency of workflow and users, acceptable downtime, and other related apps that need synchronization.
- Compliance with the defined SLAs and SLOs
Discover and absorb current documentation
Most mainframe systems have lived several decades. It is hard to find knowledge about their design and development. This situation gets augmented with many mainframe and Cobol programmers either retiring or nearing retirement.
However, finding people, documents, and videos about these applications is still possible. It helps to incite an understanding of the applications, their assets, relationships, and criticality to the business. Enterprise leaders must run a discovery campaign to unearth and comprehend this knowledge.
Define migration Roadmap
Once the infrastructure, tools, people, and other requirements are in place, it is time to develop an actionable mainframe migration project plan. Business leaders must detail migration steps from start to finish. These plans include the following actions.
- Informing the stakeholders, Preparing the users/customers
- Transferring and synchronizing the required data
- Moving the workload
- Testing and validating the shift
- Documentation for reference and troubleshooting
- Establishing contingency plans for recovery and rollback
- Opening migrated workload for users
- Monitoring workload
Moving ahead with conviction
A report predicts the global application transformation market will grow to USD 16.8 billion by 2024 with an 11.6% jump in CAGR. These figures translate the exponentially increasing gravitation of businesses towards modernization.
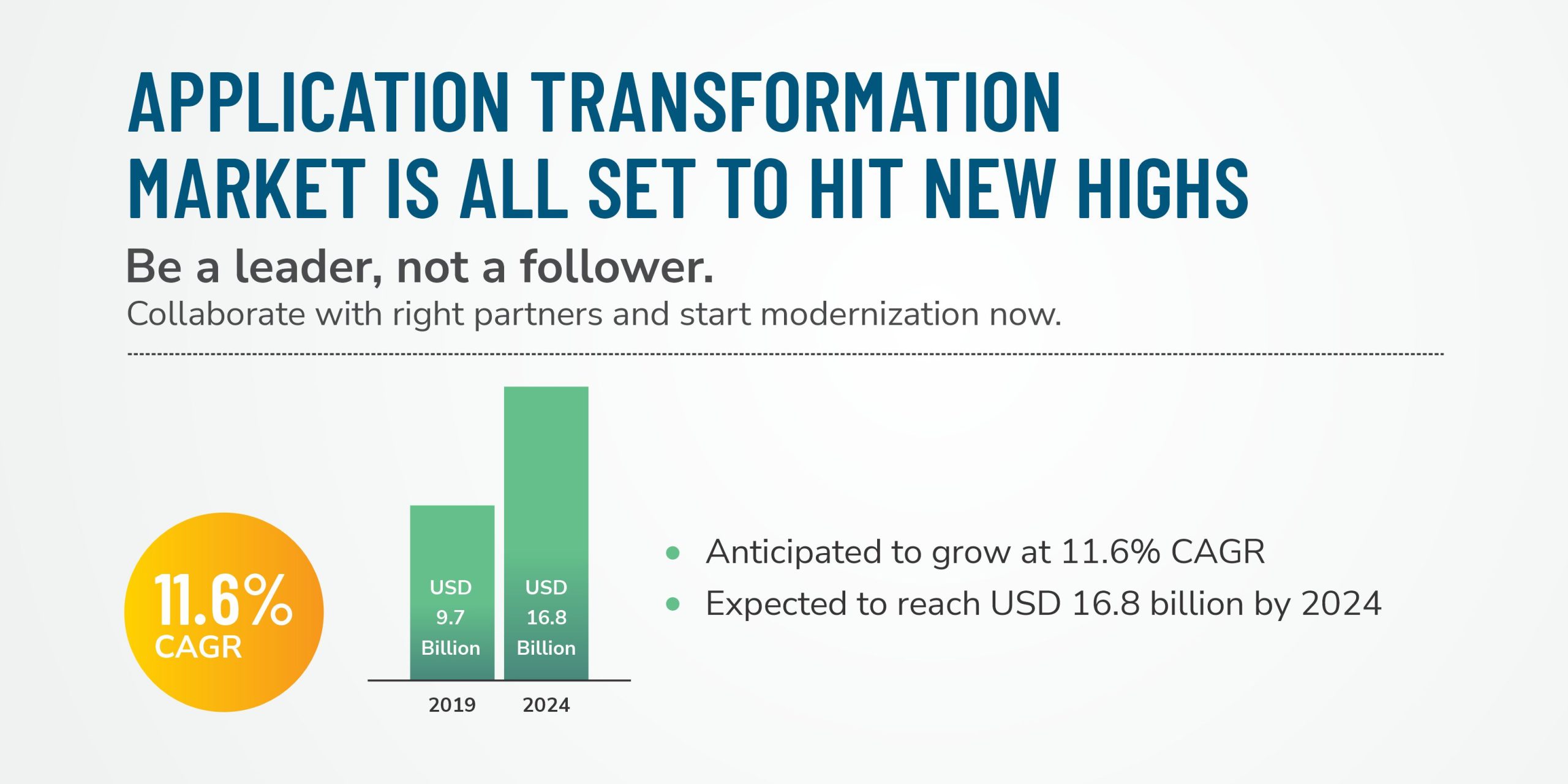
Ref: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/application-transformation-market-685357.html
While the shift is integral to staying competitive, it can be highly challenging and expensive. However, a seasoned, proficient partner can significantly simplify the journey of enterprise mobilization with the best cloud solution.
Kumaran Systems specializes in migrating mainframe applications to the cloud. Our team of accomplished professionals with profound knowledge and skills orchestrates the migration in a disciplined fashion. We ensure a smooth transition and realization of the desired business goals with predictability and precision.



